
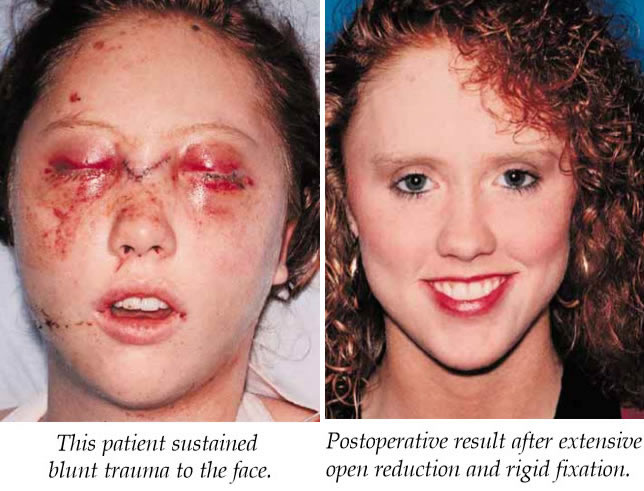
Better evaluation of each orbitofacial trauma should include preoperative evaluations both clinically and with computerized tomography. Complications were also more common with combined orbital rim fractures and medial wall and floor fractures. Of the chronic enophthalmos cases most were due to inadequate orbital volume reduction and uncorrected medial wall fractures. The impact may be mild or severe, causing the eye socket (the bony cup that surrounds and protects the eye) to become fractured or even damaging the eye itself. Of the acute complications lid malposition was the most common followed by orbital soft tissue incarceration. An orbital fracture, also known as an orbital blowout fracture, is frequently found in patients who experience trauma to their faces or skulls. When reviewed by fracture pattern, complications from orbital fractures with LeForte/Panfacial were 23/49 (47%), orbital fractures with rim 29/66 (44%) internal orbital floor/medial wall together 27/79 (34%), and internal orbital floor/medial wall alone 12/103 (11.7%). Hyperglobus had 11 (3.8%), Eyelid/soft tissue abnormalities 9 (3.1%), infection 4 (1.7%), and implant instability 4 (1.7%). Of the chronic cases, 17 (5.7%) had enophthalmos/hypoglobus from inadequate orbital volume reduction and uncorrected medial wall fractures. Of the acute 19 (6.5%) had lid malposition, 9 (3.1%) orbital soft tissue incarceration, 8 (2.7%) infection, 6 (2%) hemorrhages, 2 (0.7%) optic neuropathy, and 2 (0.7%) inappropriate return to the operating room. Of the 297 procedures 15.8% had acute complications and 15.1% chronic. Etiologies of fractures in order of frequency included assault, MVA, sports injuries, explosive devices and gun shot wounds. Acute versus chronic categories were utilized.ģ76 orbitofacial fractures of which 297 procedures on 273 patients were included. End points were measured as any worsening or objective non-improvement after surgical intervention. Exclusions included those without orbital imaging, inadequate/incomplete records and extensive fractures with difficult to measure clinical endpoints. Records had to include operative reports and pre and postoperative imaging studies. Review included only those fractures taken to the operating room, primary trauma and referral cases. Operative logs from Jan 1995 to Jan 2005 were reviewed from oculofacial trauma cases. Facial trauma services consist of oculofacial plastics, oral and maxillofacial surgery, otolaryngology, and plastic surgery. Wilford Hall Medical Center and Brook Army Medical Center are level one trauma centers in San Antonio, TX. It’s most common in teen and young males who play baseball or softball. The condition often happens after blunt injury to the face. To show the complication rates of surgical repair of orbital trauma when assessed in a level one trauma center when multiple surgical services are utilized. An orbital fracture happens when one or more bones around the eye are broken.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
